AI Governance and Compliance Frameworks 2025: Navigating NIST, EU AI Act & ISO 42001

As artificial intelligence systems become increasingly integrated into business operations and critical infrastructure, organizations face mounting pressure to implement robust AI governance frameworks. In 2025, three major frameworks are shaping the landscape of AI compliance: NIST AI RMF, the EU AI Act, and ISO/IEC 42001. Understanding how to navigate these frameworks is essential for building trustworthy, compliant AI systems.
The AI Governance Imperative
The rapid deployment of AI technologies has outpaced regulatory frameworks, creating significant risks around transparency, accountability, bias, and security. Organizations that fail to implement proper AI governance face severe consequences, including regulatory penalties up to €35 million or 7% of global revenue under the EU AI Act, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust.
🎯 Key Takeaway
Organizations must adopt a comprehensive AI compliance strategy that aligns with multiple frameworks. The question is no longer "if" but "how" to implement effective AI governance.
Understanding the Three Pillars of AI Governance in 2025
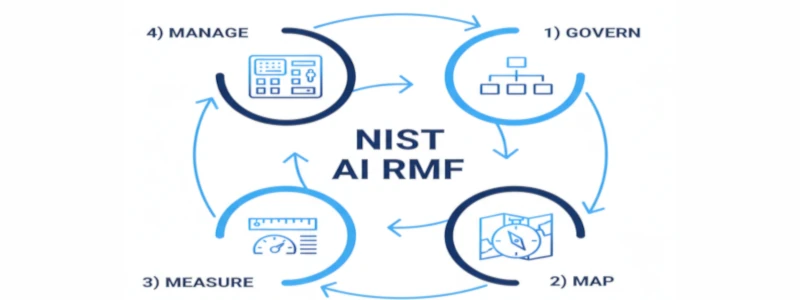
1. NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF)
Developed by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology, the NIST AI RMF provides a voluntary framework for managing risks associated with AI systems. Published in January 2023, it has quickly become a cornerstone of AI governance in the United States and internationally.
Core Principles:
- Trustworthiness - Building AI systems that are reliable and worthy of confidence
- Safety & Security - Protecting systems from malicious attacks and unintended failures
- Explainability & Interpretability - Ensuring AI decisions can be understood
- Privacy - Safeguarding personal data and user information
- Fairness - Preventing discrimination and bias in AI systems
- Accountability - Establishing clear responsibility for AI outcomes
The Four Core Functions:
- Govern - Establish policies, roles, and responsibilities for AI governance
- Map - Identify and document AI system context, risks, and impacts
- Measure - Analyze and assess AI risks using quantitative and qualitative methods
- Manage - Implement strategies to mitigate identified risks and monitor effectiveness
2. EU Artificial Intelligence Act
The EU AI Act (Regulation EU 2024/1689) represents the world's first comprehensive legal framework for artificial intelligence. It came into force on August 1, 2024, making it a legally binding regulation rather than a voluntary framework.
Risk-Based Classification System:
- Prohibited AI - Systems that pose unacceptable risks (e.g., social scoring, real-time biometric identification in public spaces)
- High-Risk AI - Systems in critical infrastructure, education, employment, law enforcement (strict compliance requirements)
- Limited-Risk AI - Systems requiring transparency (e.g., chatbots must disclose they're AI)
- Minimal-Risk AI - Most AI applications with voluntary codes of conduct
Key Compliance Requirements:
- Risk management systems and documentation
- Data governance and quality requirements
- Technical documentation and record-keeping
- Human oversight mechanisms
- Accuracy, robustness, and cybersecurity measures
- Conformity assessments and CE marking
⚠️ Penalty Alert
Non-compliance with the EU AI Act can result in fines up to €35 million or 7% of global annual turnover, whichever is higher. For prohibited AI systems, penalties reach €7.5 million or 1.5% of turnover.
3. ISO/IEC 42001:2023 - AI Management Systems
ISO/IEC 42001, published in December 2023, is the world's first international standard for Artificial Intelligence Management Systems (AIMS). Unlike regulations, it provides a certifiable framework that organizations can use to demonstrate their commitment to responsible AI.
Key Components:
- 38 Controls across 9 control objectives
- Risk and Impact Assessments - Mandatory evaluation processes
- AI System Lifecycle Management - From development to decommissioning
- Data Management - Quality, governance, and privacy controls
- Continuous Improvement - Ongoing monitoring and enhancement
Certification Process:
- Valid for 3 years with annual surveillance audits
- Re-certification required in year three
- Evaluates both documentation and operational effectiveness
- Integrates with ISO 27001, ISO 27701, and other management standards

Building a Unified AI Governance Strategy
Rather than treating these frameworks as separate compliance checkboxes, leading organizations are developing integrated governance strategies that address all three frameworks simultaneously.
Step 1: Establish AI Governance Foundations
- Create an AI governance committee with executive sponsorship
- Define roles and responsibilities (AI Ethics Officer, Data Protection Officer, etc.)
- Develop AI policies and principles aligned with NIST core values
- Implement AI system inventory and classification processes
Step 2: Conduct Risk Assessment and Classification
- Map all AI systems using NIST's Map function
- Classify systems according to EU AI Act risk categories
- Perform risk and impact assessments per ISO 42001 requirements
- Document AI system purposes, data sources, and decision logic
Step 3: Implement Controls and Safeguards
- Deploy technical controls addressing NIST's Measure and Manage functions
- Implement EU AI Act requirements for high-risk systems
- Apply ISO 42001's 38 controls across your AI portfolio
- Establish human oversight mechanisms
- Create bias detection and fairness testing protocols
Step 4: Enable Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
- Deploy automated monitoring for AI system performance and drift
- Conduct regular audits and assessments
- Maintain comprehensive documentation and audit trails
- Update risk assessments as systems evolve
- Track regulatory changes and update compliance programs
Industry Adoption and Market Trends
As of 2025, organizations across sectors are accelerating their AI governance initiatives. Market analysis indicates that ISO 42001 adoption is matching or exceeding 2024's growth trajectory, with particular interest from:
- AI Model Providers - Companies developing foundation models and AI platforms
- Cloud Service Providers - AWS, Azure, Google Cloud pursuing certification
- SaaS Companies - Especially those with high-risk AI use cases
- Regulated Industries - Healthcare, finance, and legal sectors
- Government Contractors - Organizations working with public sector clients
💡 Success Story
Microsoft achieved ISO/IEC 42001 certification in 2024, demonstrating how large-scale AI operations can implement comprehensive governance frameworks. Their approach integrates NIST AI RMF principles with ISO 42001 controls, positioning them for EU AI Act compliance.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Challenge 1: Resource Constraints
Solution: Start with a pilot program focusing on your highest-risk AI systems. Use the NIST framework's risk-based approach to prioritize efforts and demonstrate ROI before expanding.
Challenge 2: Technical Complexity
Solution: Leverage third-party AI testing and validation services like TestMy.AI to conduct independent assessments. Partner with governance platform providers to automate compliance monitoring.
Challenge 3: Regulatory Uncertainty
Solution: Implement flexible governance frameworks that can adapt to evolving regulations. Focus on fundamental principles (fairness, transparency, accountability) that will remain constant across frameworks.
Challenge 4: Cross-Border Operations
Solution: Adopt the most stringent requirements (typically EU AI Act) as your baseline, ensuring compliance across all jurisdictions. ISO 42001 certification provides global recognition.
The Future of AI Governance
Looking ahead, we expect continued convergence of AI governance frameworks globally. Additional developments on the horizon include:
- Expanded requirements for generative AI and large language models
- Industry-specific guidance and vertical standards
- Enhanced focus on AI supply chain governance
- Automated compliance monitoring and reporting tools
- Integration with ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) frameworks
Taking Action: Your Next Steps
Building effective AI governance is a journey, not a destination. Organizations should:
- Assess Current State - Conduct a gap analysis against NIST, EU AI Act, and ISO 42001
- Build Your Roadmap - Prioritize quick wins and critical compliance requirements
- Engage Stakeholders - Secure executive buy-in and cross-functional collaboration
- Implement Incrementally - Start with foundational controls and expand systematically
- Partner with Experts - Leverage specialized services for testing, auditing, and certification
Ensure Your AI Systems Are Compliant and Trustworthy
TestMy.AI provides comprehensive AI security testing and governance assessments aligned with NIST AI RMF, EU AI Act, and ISO 42001 requirements.
Get a Free AI Security AssessmentLearn About Our SolutionsReferences and Further Reading
- National Institute of Standards and Technology. (2023). "AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF 1.0)." https://www.nist.gov/itl/ai-risk-management-framework
- European Commission. (2024). "Regulation (EU) 2024/1689 - Artificial Intelligence Act." https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/regulatory-framework-ai
- International Organization for Standardization. (2023). "ISO/IEC 42001:2023 - Information technology - Artificial intelligence - Management system." https://www.iso.org/standard/42001
- Cloud Security Alliance. (2025). "How can ISO/IEC 42001 & NIST AI RMF help comply with the EU AI Act?" https://cloudsecurityalliance.org
- Lumenova AI. "AI Governance Frameworks: NIST AI RMF vs EU AI Act vs Internal." https://www.lumenova.ai/blog/
- ZenGRC. "Navigating the Future of AI Governance: A Guide to NIST AI RMF, ISO/IEC 42001, and the EU AI Act." https://www.zengrc.com/blog/